1.6: Nucleic Acids
All important biological molecules in your body are macromolecules. These include carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. There are two kinds of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA. Topic 1.6 looks at the key differences between the structure and function of these two nucleic acids.
Vocab List
- DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
- RNA (Ribonucleic acid)
- mRNA
- tRNA
- rRNA
Written Explanation
DNA and RNA are the two main types of nucleic acids. DNA is used by most organisms (excluding viruses) to store genetic information, while RNA is used to express that information (more on this in 6.3 and 6.4).
Similarities:
Both DNA and RNA share a very similar structure. They both have a 5 carbon backbone, phosphate groups, and nitrogenous bases. However the specific components used by each of them differs slightly.
Differences:
DNA:
As described in 1.5, DNA has two strands that are antiparallel. Each of these strands are composed of a chain of nucleotides, each with a nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous bases available to DNA are adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine (ATCG). They always pair up as A-T and C-G. The 5 carbon sugars of DNA are deoxyribose.
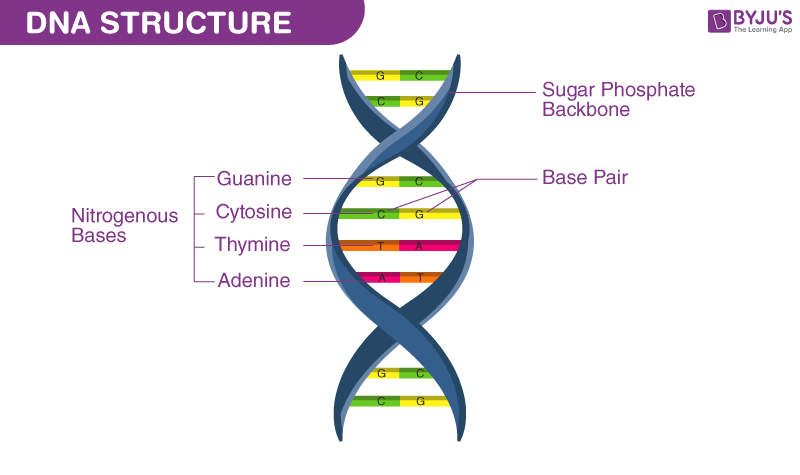 A DNA molecule. The shape formed by the twisting of the strands is called a double helix
A DNA molecule. The shape formed by the twisting of the strands is called a double helix
RNA
RNA comes in three varieties (that you need to know for now). The first is mRNA, which is very similar to DNA. mRNA means messenger RNA.
mRNA's nitrogenous bases are adenine, uracil, cytosine, and guanine (AUCG). Its bonding pattern is A-U and C-G (functionally, uracil is identical to thymine, but don't confuse them). The 5 carbon sugars of all RNAs are ribose, unlike DNA's deoxyribose. The function of mRNA is to carry transcribed DNA to ribosomes (where the information will be turned into a protein). Lastly, RNA is single stranded, not double stranded like DNA.
 A diagram of mRNA next to its 4 possible nitrogenous bases
A diagram of mRNA next to its 4 possible nitrogenous bases
Another type of RNA is tRNA. tRNA is used in ribosomes to translate mRNA into amino acids/proteins. This will be covered in more detail in unit 6. rRNA is a component of ribosomes that facilitates the translation of mRNA. These three nucleic acids are crucial to your body's function, but for this unit, this is all you need to know.